One of the first malware samples tailored to run natively on Apple’s M1 chips has been discovered, suggesting a new development that indicates that bad actors have begun adapting malicious software to target the company’s latest generation of Macs powered by its own processors.
While the transition to Apple silicon has necessitated developers to build new versions of their apps to ensure better performance and compatibility, malware authors are now undertaking similar steps to build malware that are capable of executing natively on Apple’s new M1 systems, according to macOS Security researcher Patrick Wardle.
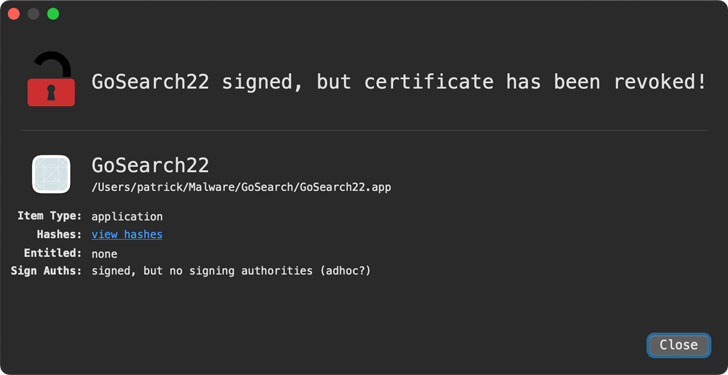
Wardle detailed a Safari adware extension called GoSearch22 that was originally written to run on Intel x86 chips but has since been ported to run on ARM-based M1 chips. The rogue extension, which is a variant of the Pirrit advertising malware, was first seen in the wild on November 23, 2020, according to a sample uploaded to VirusTotal on December 27.
“Today we confirmed that malicious adversaries are indeed crafting multi-architecture applications, so that their code will natively run on M1 systems,” said Wardle in a write-up published yesterday. “The malicious GoSearch22 application may be the first example of such natively M1 compatible code.”
While M1 Macs can run x86 software with the help of a dynamic binary translator called Rosetta, the benefits of native support mean not only efficiency improvements but also the increased likelihood of staying under the radar without attracting any unwanted attention.
First documented in 2016, Pirrit is a persistent Mac adware family notorious for pushing intrusive and deceptive advertisements to users that, when clicked, downloads and installs unwanted apps that come with information gathering features.
The heavily obfuscated GoSearch22 adware disguises itself as a legitimate Safari browser extension when in fact, it collects browsing data and serves a large number of ads such as banners and popups, including some that link to dubious websites to distribute additional malware.
Wardle said the extension was signed with an Apple Developer ID “hongsheng_yan” in November to conceal its malicious content further, but it has since been revoked, meaning the application will no longer run on macOS unless attackers re-sign it with another certificate.
Although the development highlights how malware continues to evolve in direct response to both hardware changes, Wardle warned that “(static) analysis tools or antivirus engines may struggle with arm64 binaries,” with detections from industry-leading security software dropping by 15% when compared to the Intel x86_64 version.
GoSearch22’s malware capabilities may not be entirely new or dangerous, but that’s beside the point. If anything, the emergence of new M1-compatible malware signals this is just a start, and more variants are likely to crop up in the future.