Threat actors have been found using a previously undocumented JavaScript malware strain that functions as a loader to distribute an array of remote access Trojans (RATs) and information stealers.
HP Threat Research dubbed the new, evasive loader “RATDispenser,” with the malware responsible for deploying at least eight different malware families in 2021. Around 155 samples of this new malware have been discovered, spread across three different variants, hinting that it’s under active development.
“RATDispenser is used to gain an initial foothold on a system before launching secondary malware that establishes control over the compromised device,” security researcher Patrick Schläpfer said. “All the payloads were RATs, designed to steal information and give attackers control over victim devices.”
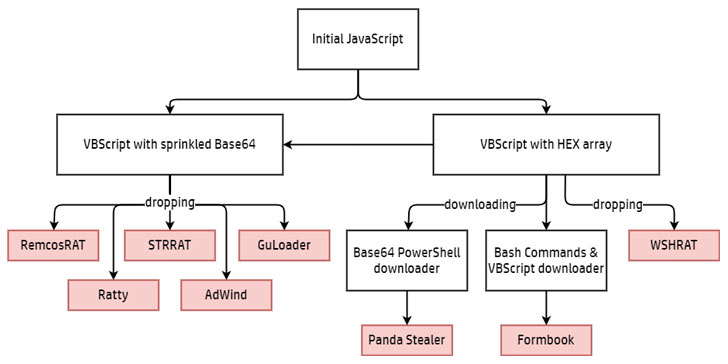
As with other attacks of this kind, the starting point of the infection is a phishing email containing a malicious attachment, which masquerades as a text file, but in reality is obfuscated JavaScript code programmed to write and execute a VBScript file, which, in turn, downloads the final-stage malware payload on the infected machine.
RATDispenser has been observed dropped different kinds of malware, including STRRAT, WSHRAT (aka Houdini or Hworm), AdWind (aka AlienSpy or Sockrat), Formbook (aka xLoader), Remcos (aka Socmer), Panda Stealer, CloudEyE (aka GuLoader), and Ratty, each of which are equipped to siphon sensitive data from the compromised devices, in addition to targeting cryptocurrency wallets.
“The variety in malware families, many of which can be purchased or downloaded freely from underground marketplaces, and the preference of malware operators to drop their payloads, suggest that the authors of RATDispenser may be operating under a malware-as-a-service business model,” Schläpfer said.